ISJ Exclusive: Security by design


James Thorpe
Share this content
Anthony Fitze and Carl Fenger of LEGIC Identsystems describe how to effectively establish trust in the Industrial Internet of Things.
In industrial environments, mass deployment of sensors and the ability to securely collect and process data from fixed and mobile assets significantly increases efficiency and enables better business decisions. It makes it easier to streamline processes, reduce errors, support auditing and enforce quality control.
The common denominator: Trust
Simply connecting sensors to the internet is not enough. The viability of processes improved by the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) depends on a common denominator: Trust. Without the ability to trust data, sensors and the people who access them, IIoT deployments lose their effectiveness. If users, sensors and interactions cannot be trusted, the results can be costly and catastrophic, especially where volatile assets and human safety are involved, which is often the case.
The three pillars of trust in the IIoT
Being able to trust in IIoT data relies on linking verified users with trusted sensors/objects so that interactions are reliable, transparent and accountable. Accomplishing this relies on three principles:
- Accountability: Users must be identifiable and accountable before gaining access to sensors or infrastructure. Access permissions must be assigned based on roles, training and authorisations plus context-based criteria such as time, location and environmental data. Permissions must be autonomously enforced, both online and offline, to minimise human error and support 24/7 operation. All activities must be transparent and auditable.
- Security: Equipment must only be configured and accessed by authorised users. Devices must be immune to spoofing. As sensors are the most vulnerable component of an IIoT system, physical hardware-level security must be implemented in the form of an embedded Secure Element for hosting of encryption keys and user permissions.
- Transparency: Interactions between users and devices and the data they generate must be trustable and transparent to validated users. They must not be visible to, nor subject to manipulation or interception by unauthorised parties either at the sensor, along local area networks, air interfaces or over the network, including the publicly available internet.
Pillar 1: Accountability
To establish accountability, IIoT system users must be verified to establish trust. Permissions to access physical areas, machines, vehicles, functionalities and information must be granted based on each trusted user’s credential. Credentials define where a user is allowed to go and when, what machines and their functionality are allowed to be used based on their training and function, which storage containers they can open, etc.
Users change regularly – employees come and go, change job function or complete training on a daily basis. External auditors or contractors require ad-hoc credentials on a time-limited basis. Permissions must be able to be created and reconfigured in real time and over-the-air. The system must function in both online and offline modes as network connections are not always available or reliable.
Important requirements include the real time updating of credentials as well as adding and removing staff at the touch of a button. These can all be supported by a mobile app on devices such as iOS/Android smartphones or tablets.
Pillar 2: Security
Trusted data only comes from trusted sensors. As IIoT deployments have thousands of sensors spread over large areas, deployment, configuration, management and readout must be easy, quick and cost-effective. Ease of device retrofit is also important as many existing industrial installations need quick upgrading in-place.
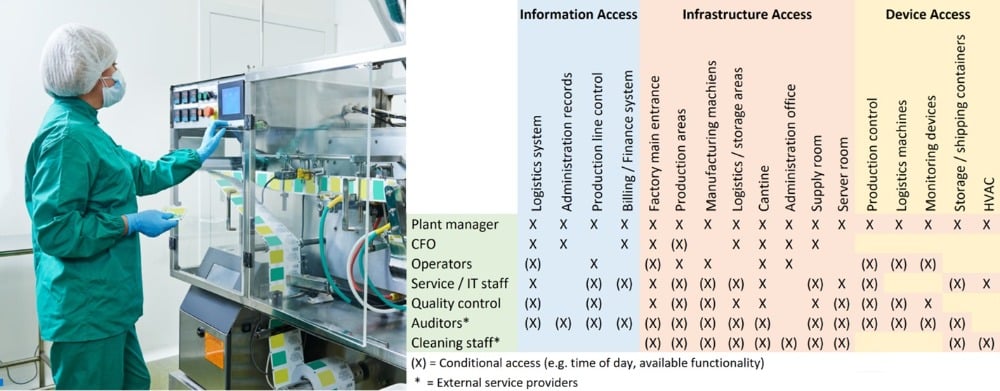
LEGIC Connect mobile credentialing platform for IIoT system users
LEGIC Connect is a mobile credentialing platform that securely distributes mobile credentials or other data to registered smartphones or tablets anytime, anywhere and instantly at the touch of a button. The system provides a globally available, secure, end-to-end mobile credentialing service that is the backbone of establishing trust and accountability in user/sensor/infrastructure interactions.
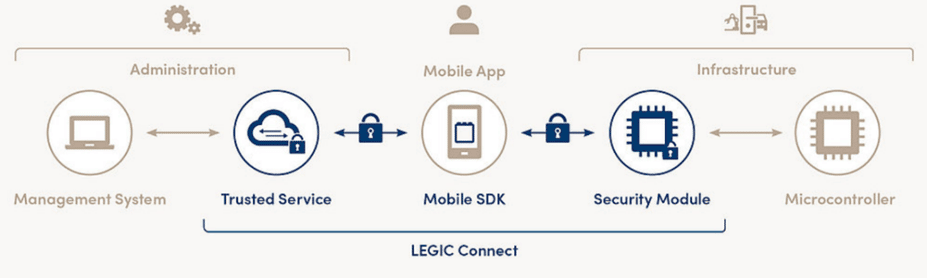
The system can be easily integrated into existing industrial infrastructure, giving IIoT service operators the ability to manage user permissions as well as send and receive data securely from smartphones and sensors.
Establishing a trusted device network relies on these attributes:
- All sensor data must be protected by the highest commercially available level of encryption such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
- Encryption keys must be invisible during initialisation and inaccessible during operation. Encryption keys and other sensitive data must be stored in a physically and electronically inaccessible secure element embedded in the sensor. During device initialisation, encryption keys must never be human readable either at rest or in transit
- Infrastructure spoofing must be impossible (e.g., a sensor which has been maliciously replaced with a manipulated sensor). A unique, invisible encryption key embedded in a secure element at each sensor prohibits this from occurring: Without the key, sensors will not respond
- Wireless access is necessary: Because sensors are often installed in hard to reach areas, encrypted wireless communications is necessary over RFID, Bluetooth Low Energy or NFC via smartphone
- Firmware update over-the-air is required: Configuration and updating of sensors in the field must be possible; factory programming should be avoided to keep deployment and logistics costs down. This also increases security as third party manufacturers are not involved
- Sensors and access to them must operate both online and offline: The system must function even with no network connection to ensure continuous operations
- Sensors must be modular, off-the-shelf and configurable in the field: This streamlines device supply chains and minimizes opportunities for manipulation during manufacturing. It also allows for ease of custom configurations in the field while allowing the administrator of the IoT deployment to operate independently from sensor suppliers.
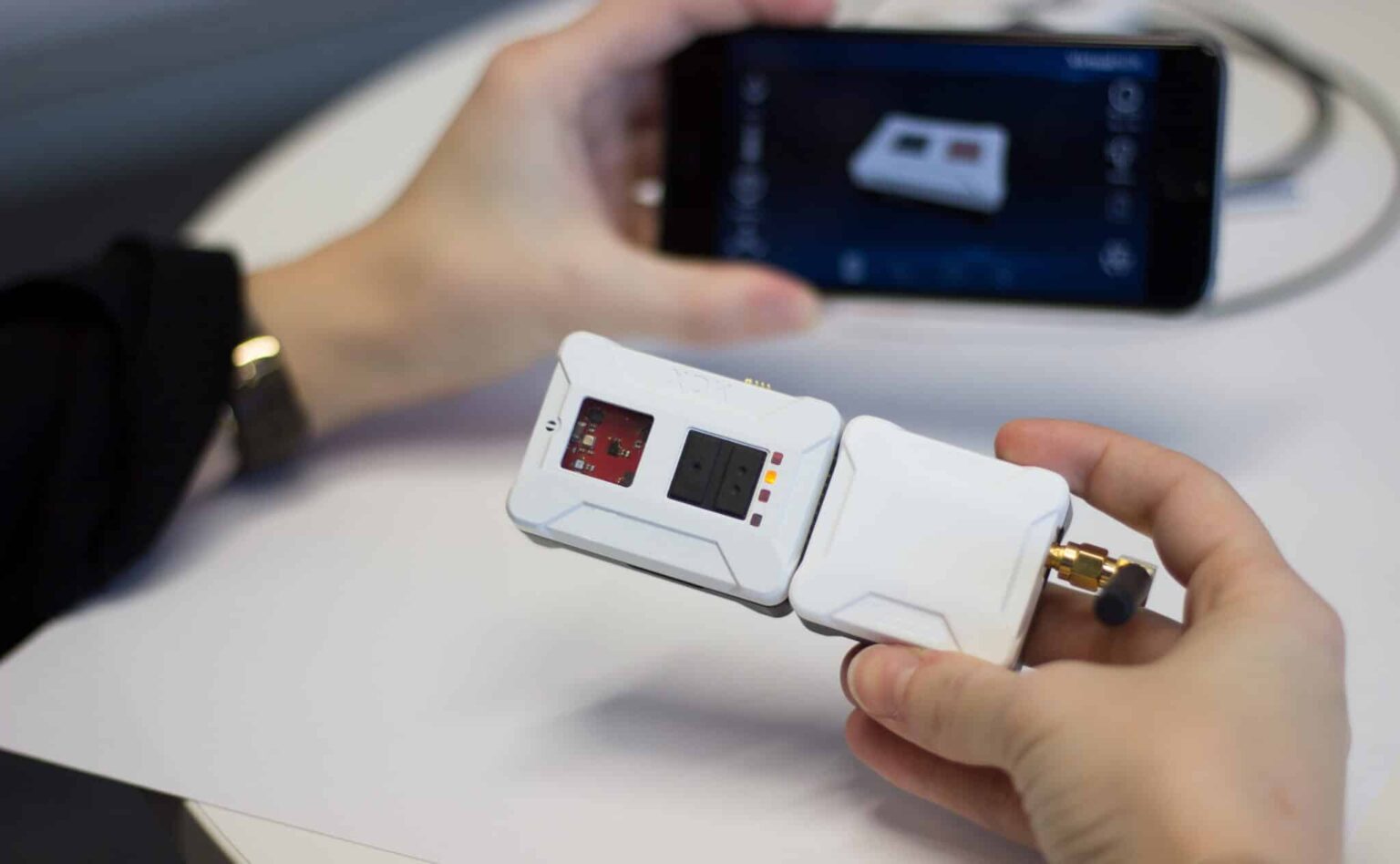
LEGIC XDK
The LEGIC XDK Secure Sensor development Evaluation Kit is the “The Swiss army knife of IoT solutions”. The kit is a universal programmable sensor device and prototyping platform for any IoT use case you can imagine. It includes a LEGIC Security Module which enables sensor configuration and readout via mobile devices which can be configured in real time from the cloud for user authentication and sensor access permissioning.
With built-in integrated Secure Element for storage of cryptographic keys/whitelists and wireless communications, it enables rapid prototyping of highly secure, touchless, sensor-based products and IoT applications.
- All-in-one sensor kit: no need for component selection, hardware assembly or deployment of a real time operating system
- Operates with LEGIC Connect for secure, end-to-end management of mobile credentials (Android & iOS)
- Includes accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer, environmental sensors (humidity, temperature, air pressure), ambient light and a microphone for noise detection, together with Wi-Fi, Bluetooth® Low Energy and an SD card slot
- Software examples and development APIs included
Pillar 3: Transparency
With trust in users and sensor security established, transparency is achieved by verified users securely collecting and managing data from trusted devices over an encrypted network for processing by a management system. As IIoT deployments comprise sensors distributed over a wide area, or in mobile containers that could be anywhere, being able to trust data as it traverses multiple wireless, cellular and internet links is crucial.
As no network can be 100% protected against data interception, end-to-end encryption must be employed. Using managed AES encryption, the most powerful commercially available encryption protocol, even networks susceptible to data interception cannot be meaningfully hacked as the payload in each data packet is impossible to read without the encryption key. Encryption keys are never visible either in-transit or at rest.
LEGIC Orbit enables system-wide data security and transparency
Based on managed end-to-end AES encryption, LEGIC Orbit is an intrinsic part of LEGIC’s Security Platform which enables you to securely operate your IoT solutions. LEGIC Orbit secures LEGIC’s credentialing technology which is at the heart of your mobile IoT solution. It also protects messaging from your sensor modules back to your IoT management system.
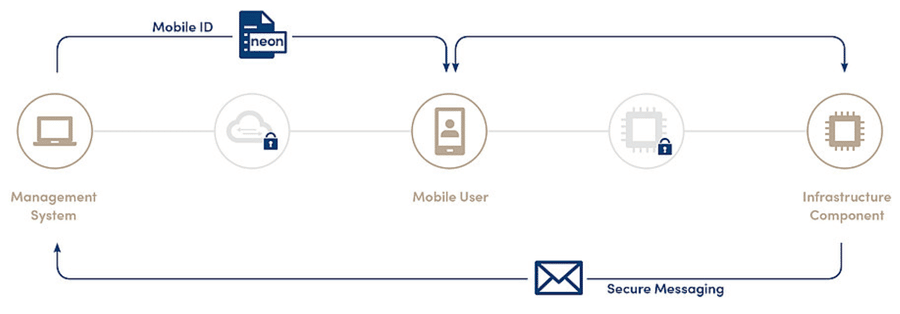
A secure gatekeeper at the IIoT edge
With a secure, end-to-end IIoT platform based on mobile credentialing, managed encryption and secure element technologies, accountability, security and transparency can be achieved. Updateable user credentials combined with context-based information makes tasks easier and safer while improving process quality, integrity, accountability and convenience.
Some specific use cases include:
- Logistics automation: A trusted IIoT platform enables secure and transparent movement of goods within as well as between facilities by securing access and logging interactions and states during transportation. Authorised transport of goods within a facility is further enhanced by indoor positioning systems
- Building management: Linking of persons with a verified identity enables trusted monitoring of building assets and interactions between users and doors, HVAC systems, security systems, fire alarms, indoor navigation systems and more. Location-triggered automated processes can be implemented based on user identity and managed via centralised, digitally distributed access rights and permissions
- Industrial equipment: Linking of persons with a verified identity followed by dynamic permissioning and access to equipment ensures trusted interactions and accountability. Industrial equipment can be reliably located, identified and monitored. Protocolled equipment usage data can be collected per user. Granting and restriction of permissions can be performed in real time and over-the-air
The LEGIC IIoT Security Platform can be integrated with any application and in any infrastructure. For more details about deploying trust based IIoT sensors and systems visit: www.legic.com/iot
This article was originally published in the November edition of International Security Journal. To read your FREE digital edition, click here.



